数据结构和算法
栈
栈的应用
1、把十进制数转为二进制数
// 函数:将十进制转成二进制
// 十进制 二进制
// Decimal binary
function dec2bin(decNumber) {
// 1、定义栈对象
let stack = new Stack();
// 2、循环操作
while (decNumber > 0) {
// 2.1、获取余数,并且放入到栈中
stack.push(decNumber % 2);
//2.2、获取整除后的结果,作为下一次运行的数字
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / 2);
}
// 3、从栈中取出0和1
let binaryString = '';
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
binaryString += stack.pop();
}
return binaryString;
}
//测试十进制转二进制的函数
console.log(dec2bin(5)); //101
console.log(dec2bin(50)); //110010队列(queue)
只允许在一端插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表;
进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(入队列),进行删除操作的一端称为队头(出队列);队列具有先进先出(FIFO)的特性。
js 队列的实现(线性存储)
//封装队列类
function Queue() {
//队列中的属性
this.items = [];
//栈的相关操作
// 1、将元素加入到队列中
Queue.prototype.add = function (element) {
this.items.push(element);
};
// 2、从队列中删除前端元素
Queue.prototype.delete = function () {
return this.items.shift();
};
//3、查看队列前端元素
Queue.prototype.front = function () {
return this.items[0];
};
// 4、判断队列是否为空
Queue.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.items.length == 0;
};
// 5、获取队列中元素的个数
Queue.prototype.size = function () {
return this.items.length;
};
// 6、toString方法
Queue.prototype.toString = function () {
let resultString = '';
for (let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
resultString += this.items[i] + ' ';
}
return resultString;
};
}
//队列的使用
let q = new Queue();
q.add('22');
q.add('33');
q.add('44');
q.delete();
console.log(q);
console.log(q.size());
console.log(q.front());
console.log(q.isEmpty());链表结构
- 多个元素组成的列表。
- 元素存储不连续,用 next 指针连在一起。
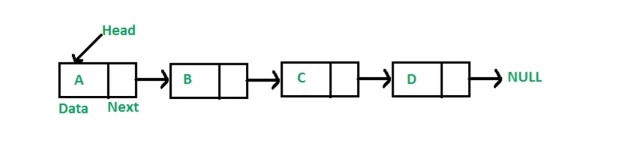
数组 vs 链表
- 数组:增删非首尾元素是往往需要移动元素。
- 链表:增删非首尾元素,不需要移动元素,只需要更改 next 的指向即可。
集合
- 一种无序且唯一的数据结构
- ES6 中有集合,名为 set
- 集合的常用操作:去重,判断某元素是否在集合中、求交集
//使用set对象
let mySet = new Set();
mySet.add(1);
mySet.add(5);
mySet.add(5);
mySet.add('some text');
let o = { a: 1, b: 2 };
mySet.add(o);
mySet.add({ a: 1, b: 2 });
//是否存在该元素
const has = mySet.has(o);
mySet.delete(5);
//遍历
for (let item of mySet) {
console.log(item);
}
//转换成数组
const myArr = [...mySet];
const myArrs = Array.from(mySet);
const mySet2 = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4]);
//求交集
const intersection = new Set([...mySet].filter((x) => mySet2.has(x)));
//求并集
const difference = new Set([...mySet2].filter((x) => !mySet2.has(x)));字典
字典是以[键,值]的形式来存储元素。字典也称作映射、符号表或关联数组。
集合、字典、散列表都可以存储不重复的数据。字典和我们上面实现的集合很像。
ES5 包含了一个 Map 类的实现,即我们所说的字典。
const m = new Map();
//增
m.set('a', 'aa');
m.set('b', 'bb');
//删
m.delete('b');
// m.clear();
//改
m.set('a', 'aaa');
//查
m.get(a);两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
var twoSum = function (nums, target) {
const map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
const n = nums[i];
const n2 = target - n;
if (map.has(n2)) {
return [map.get(n2), i];
} else {
map.set(n, i);
}
}
};
const nums = [4, 5, 6, 7],
target = 9;
twoSum(nums, target);树
一种分层数据的抽象模型
前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM、树、级联选择、树形控件
JS 中没有树,但是可以用 Object 和 Array 构建树
树的常用操作:深度/广度优先遍历、先中后序遍历
深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支
广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点
深度优先遍历算法口诀
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的 children 挨个进行深度优先遍历
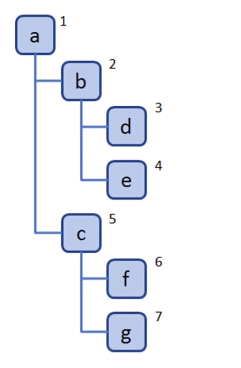
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: [],
},
{
val: 'e',
children: [],
},
],
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: [],
},
{
val: 'g',
children: [],
},
],
},
],
};
const dfs = (root) => {
console.log(root.val);
root.children.forEach(dfs);
};
dfs(tree);广度优先遍历算法口诀
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队。
- 把队头出队并访问。
- 把队头的 children 挨个入队
- 重复第二、三步,直到队列为空。
const bfs = (root) => {
const q = [root];
while (q.length > 0) {
const n = q.shift();
console.log(n.val);
n.children.forEach((child) => {
q.push(child);
});
}
};
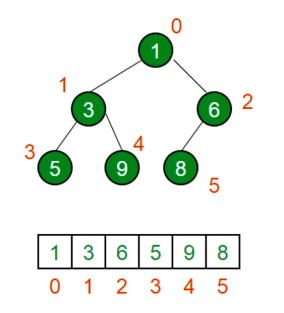
bfs(tree);二叉树是什么?
- 树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点。
- 在 JS 中通常用 Object 来模拟二叉树。
先序遍历算法口诀
访问根节点。
对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历。
对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历。
const bt = { val: 1, left: { val: 2, left: { val: 4, left: null, right: null, }, right: { val: 5, left: null, right: null, }, }, right: { val: 3, left: { val: 6, left: null, right: null, }, right: { val: 7, left: null, right: null, }, }, }; module.exports = bt; const bt = require('./bt'); //先序遍历算法 const preorder = (root) => { if (!root) { return; } console.log(root.val); preorder(root.left); preorder(root.right); }; preorder(bt); //函数调用堆栈,先序遍历非递归版 const preorder = (root) => { if (!root) { return; } const stack = [root]; while (stack.length) { const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val); if (n.right) { stack.push(n.right); } if (n.left) { stack.push(n.left); } } }; preorder(bt);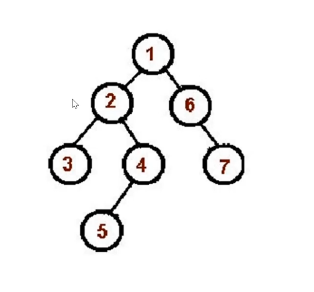
中序遍历算法口诀
对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历。
访问根节点。
对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历。
const bt = require('./bt');
//中序遍历算法
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left);
console.log(root.val);
inorder(root.right);
};
inorder(bt);
//中序遍历算法,非递归版
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
const stack = [];
let p = root;
while (p || stack.length) {
while (p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
p = n.right;
}
};
inorder(bt);后序遍历算法口诀
- 对根节点的左子树进行后序遍历。
- 对根节点的右子树进行后续遍历。
- 访问根节点。
const bt = require('./bt');
//后续遍历算法口诀,递归版
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
console.log(root.val);
};
postorder(bt);
//后续遍历算法,非递归版
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
const outputStack = [];
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop();
outputStack.push(n);
if (n.left) {
stack.push(n.left);
}
if (n.right) {
stack.push(n.right);
}
}
while (outputStack.length) {
const n = outputStack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
}
};
postorder(bt);图
- 图是网络结构的抽象模型,是一组由边连接的节点。
- 图可以表示任何二元关系,比如道路、航班
图是什么
- JS 中没有图,但是可以用 Object 和 Array 构建图
- 图的表示法:领接矩阵、邻接表、关联矩阵
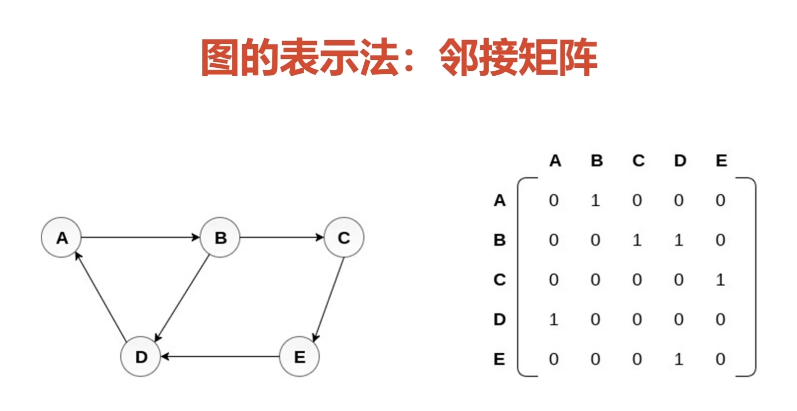
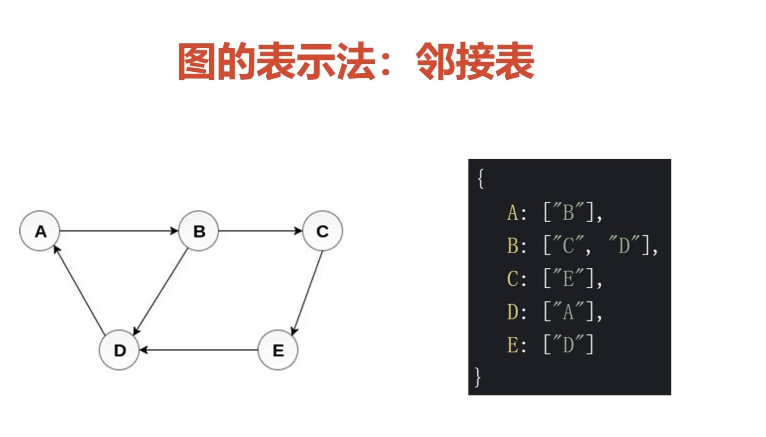
图的常用操作
深度优先遍历
尽可能深的搜索图的分支。
广度优先遍历
先访问离根节点最近的节点。
深度优先遍历算法口诀
- 访问根节点。
- 对根节点的没访问过的相邻接点挨个进行深度优先遍历。
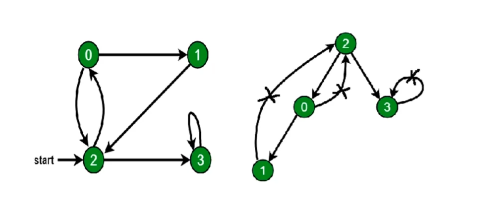
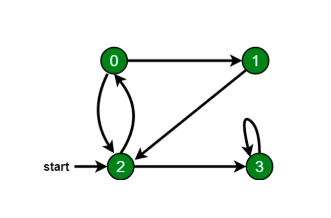
广度优先遍历算法口诀
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队。
- 把队头出队并访问。
- 把队头的没访问过的相邻节点入队。
- 重复第二三步,直到队列为空。
堆
- 堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树
- 所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)它的子节点
JS 中的堆
- JS 通常用数组表示堆。
- 左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1。
- 右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2。
- 父节点位置是(index - 1) / 2。
堆的应用
- 堆能高效、快速地找出最大值和最小值
- 时间复杂度:o(1);
- 找出第 k 个最大(小)元素
第 k 个最大元素
- 构建一个最小堆,并将元素依次插入堆中。
- 当堆的容量超过 k,就删除堆顶。
- 插入结束后,堆顶就是第 K 个最大元素。
JavaScript:冒泡排序
- 比较所有相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换他们。
- 一轮下来可以保证,最后一个数是最大的。
- 执行 n-1 轮,就可以完成排序。
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) {
const temp = this[j];
this[j] = this[j + 1];
this[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return this;
};
let arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
arr.bubbleSort(); //return [1,2,3,4,5]
//逆序则把if里的>换成<JavaScript:选择排序
- 找到数组中的最小值,选中它并将其放置在第一位
- 接着找到第二小的值,选中它并将其放置在第二位
- 以此类推,执行 n-1 轮。
Array.prototype.selectionSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
let indexMin = i;
for (let j = i; j < this.length; j += 1) {
if (this[j] < this[indexMin]) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
if (indexMin !== i) {
const temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[indexMin];
this[indexMin] = temp;
}
}
console.log(this);
};
let arr = [5,4,3,2,1]
arr.selectionSort(); //return [1,2,3,4,5]JavaScript:插入排序
- 从第二个数开始往前比。
- 比他大就往后排。
- 以此类推进行到最后一个数。
Array.prototype.insertionSort = function () {
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
const temp = this[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0) {
if (this[j - i] > temp) {
this[j] = this[j - i];
} else {
break;
}
j -= i;
}
this[j] = temp;
}
return this;
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
console.log(arr.insertionSort());JavaScript:归并排序
时间复杂度 O(n*logn)
- 分:把数组劈成两半,再递归地对数组进行“分”操作,直到分成一个个单独的数。
- 合:把两个数合并为有序数组,再对有序数组进行合并,直到全部子数组合并为一个完整数组。
合并两个有序数组
- 新建一个空数组 res,用于存放最终排序后的数组。
- 比较两个有序数组的头部,较小者出队并推入 res 中。
- 如果两个数组还有值,就重复第二步。
Array.prototype.mergeSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
const left = arr.slice(0, mid);
const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length);
const orderLeft = rec(left);
const orderRight = rec(right);
const res = [];
while (orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) {
if (orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) {
res.push(
orderLeft[0] < orderRight ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift()
);
} else if (orderLeft.length) {
res.push(orderLeft.shift());
} else if (orderRight.length) {
res.push(orderRight.shift());
}
}
return res;
};
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
return res;
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
console.log(arr.mergeSort());
//分的时间复杂度O(logN)
//合的时间复杂度是O(n);
//总的时间复杂度是O(n*logN)JavaScript:快速排序
- 分区:从数组中任意选择一个“基准”,所有比基准小的元素放在基准前面,比基准大的元素放在基准的后面。
- 递归:递归地对基准前后的子数组进行分区。
- 时间复杂度
- 递归的时间复杂度是 O(logN)
- 分区操作的时间复杂度是 O(n)
- 时间复杂度 O(nlogN)
Array.prototype.quickSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const left = [];
const right = [];
const mid = arr[0];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < mid) {
left.push(arr[i]);
} else {
right.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)];
};
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
return res;
};
const arr = [2, 4, 5, 3, 1];
console.log(arr.quickSort());JavaScript 实现:二分搜索
思路
- 从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索结束。
- 如果目标值大于或者小于中间元素,则在大于或小于中间元素的那一半数组中搜索。
时间复杂度:O(logN)
Array.prototype.binarySearch = function (item) {
let low = 0;
let high = this.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const element = this[mid];
if (element < item) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (element > item) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
};
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].binarySearch(4);
console.log(res);分而治之
- 分而治之是算法设计中的一种方法。
- 它将一个问题分成多个和原问题相似的小问题,递归解决小问题,再将结果合并以解决原来的问题。
场景一:归并排序
- 分:把数组从中间一分为二。
- 解:递归地对两个子数组进行归并排序。
- 合:合并有序子数组。
场景二:快速排序
- 分:选基准,按基准把数组分成两个子数组。
- 解:递归地对两个子数组进行快速排序。
- 合:对两个子数组进行合并。